Education System
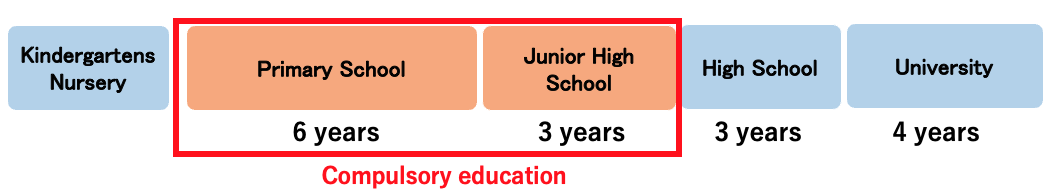
Japanese education adopts a 6-3-3-4-year educational framework.
Children are required to attend school compulsory for a minimum of 9 years as follows : Education from Grade 1 to 6 at elementary school (Primary) and Grade 1 to 3 at junior high school (Lower Secondary School), also called as Chuugakko in Japan.
More specifically, before schooling, children go to Preschool : Kindergartens (Yochien) or Nursery Centers (Hoikuen) until 5-6 years of age.
After they turn 6-7 years old, children go to Elementary School for 6 years from 1st to 6th Grade.
After the Elementary School, they go to Junior High School for 3 years from 1st year to 3rd year.
Following it many students may opt to go to High School for a period of 3 years from 1st year to 3rd year. Around the age of 18 years, when students have finished their schooling, they go for higher education (university) for a duration of 4 years, go for other types of schools (junior collage etc.), or start working.
According to Gender Equality Bureau Cabinet Office’s data, the high school enrollment rate is over 90% after the 1980s and there doesn’t seem to be a gap between boys and girls. On the other hand, in terms of enrollment rate for university, the percentages are 57.7% and 50.9% respectively for boys and girls. Both rates are rising year by year, and the gender gap is also narrowing.
| Gender | High School Enrollment Rate | University Enrollment Rate |
| Boys | 95% | 57.7% |
| Girls | 95% | 50.9% |
Source: Made by Shin Edupower based on Gender Equality Bureau Cabinet Office’s data.
Types of schools

Government School
Majority of children go to government elementary and junior high schools that are close to their home. The reason why many parents choose government schools is that the tuition fee is free. They also have places to take care of students after school, therefore it is very helpful for busy parents who come home late.
To enter government schools during the compulsory education period, children do not need to take any exams, but it is necessary to live in district areas. For example, students who go to elementary or junior high school in Tokyo, they have to live somewhere in Tokyo. Even if they live in a prefecture that is close to Tokyo, they are not allowed to go schools in that area. In addition to this, most elementary schools do not have school uniforms and any regulations for their clothes to wear. On the other hand, most junior high schools have school uniforms and have some limitations such as length of skirts and color of socks. Recent Japanese educational reforms have led to the introduction of ICT devices for each student even in government schools.
Although government based elementary and junior high schools do not take any entrance examination, but in government based high schools and universities it is necessary to take the entrance examination and pass.
Private School
Other than government schools, some children go to private elementary and junior high schools, especially in urban areas.
The biggest difference between private schools and government schools is that their tuition is much higher than government schools. As a result, private schools have more resources and flexibility. Since there are more than 2000 private schools in Japan, they need to have originality and strengths that can appeal to parents and children. So, many schools are putting efforts to employ capable teachers and raise the quality of teaching. Furthermore, in terms of environment, many private schools have sufficient equipments for classes and club activities, such as providing iPads for every student and setting lights on the sports fields so that students can practice longer.
To enter private schools, children must take exams and pass them. In order to get in, children have to go to cram schools since they are little and will need to study very hard. Nevertheless, many private schools connect to junior high or high schools, and students will not have to take entrance exams to be in higher schools. It is becoming very familiar to be in private schools since elementary or junior high school, especially in urban areas.
Entrance Examination

Elementary School
Entrance exams for private elementary school differ from school to school. So, in this section we will look at exams that majority of the elementary schools use.
Firstly, most elementary schools provide tests that examine whether children can follow teachers’ instructions. This type of exam will be held in various ways such as an interview test and an exercise test. In addition to this, it is very common to see children’s behaviors in the test. For example, there is a kind of test that is held with other children. In that group test, schools see how they interact with others and whether they use polite words and greet them nicely. These types of exams which are mentioned above usually see how parents raise their children. Therefore, it is necessary for parents to put efforts in order to pass.
Junior High School
Even though junior high school is compulsory education, private schools and government schools which connect with high school have examinations to enter.
Entrance exams for junior high schools also differ by each school when it comes to private schools. Since they create their own exams, styles and degree of difficulty differ. One common thing is that in most private schools’ exams, they have to take Japanese, Mathematics, Science and Social Studies. They basically demand students to be knowledgeable and that they can utilize their knowledge when they solve questions. Meanwhile, government schools have a unique style of examination. For instance, government schools in Tokyo have an exam called aptitude test and short essay. This test measures if students are able to use their knowledge and explain logically to others.
High School
Since high school is not part of compulsory education, students must take exams to enter any type of high school.
Between private and government schools, there are big differences about their entrance exams. In private schools, students have to take three subject exams which are Japanese, Mathematics and English. Some schools have interview tests. Most private schools create their own exams based on their standard score, therefore degree of difficulty and types of questions vary in each school.
On the other hand, government high schools have 5 subjects tests which are Japanese, Mathematics, English, Science and Social Studies. Government schools are owned by each prefecture’s local government, and usually use the same exams provided by prefectures’ board of education. Since all government schools’ exams are held on the same day, students can choose only one school to apply to. Usually students select their schools to take entrance examinations based on their standard score and schools’ characteristics.
There are many kinds of differences; however, in the exam, multiple choice questions are very common in any type of test in private and government high schools.
University
Since university is not compulsory as well, students need to take exams to get in. For entering a university, there are 3 types of exams which are exams for candidates recommended by high school principals, comprehensive entrance exams and general entrance examinations. Number of students who take exams for candidates recommended by high school principals are limited, since these types of tests need recommendation from teachers and need to have higher grades in every subject.Comprehensive entrance exams are demanding for students who match universities’ admissions policies and have knowledge and abilities that fulfill the level of university. For example, whether they can express their opinions positively and whether they have interests and knowledge about social problems or not. This type of exam is held with an essay and interview test.
Finally, general entrance examinations are basically the paper tests which the majority of students take to enter university. If they apply to a private university, they will have to take tests created by each institution and if it is for a national university, they need to get scores that are set by each university in the common university entrance exam.
Before Schooling
Before enrolling their children in compulsory education starting with elementary school, most parents in Japan send their children to a preschool – Kindergarten (Yochien) or a Nursery School (Hoikuen). Each facility has different targets, methods, aims and educational contents.
Summary

The Japanese education system follows a 6-3-3-4-year framework, with compulsory schooling spanning 9 years. Children typically attend preschool until 5-6 years old, then proceed to 6 years of elementary school and 3 years of junior high. High school is optional, followed by 4-year university education. The gender gap of the university entry rates is narrowing year by year.
Government schools are popular due to free tuition and convenient facilities, while private schools offer enhanced resources. Entrance exams vary across levels, assessing knowledge and behavior.
Preschools serve as preparatory steps, with Kindergartens and Nursery Schools offering diverse educational approaches.
There are many different types of schools in Japan, which support students learning journey.
For those who want to know more about Japanese education
Shin Edupower provides programs that enable online exchange and collaboration between schools in India and Japan, as well as study tours to Japan for educators and students. If you would like to know more about education in Japan, please feel free to contact us here.




Pingback: Exploring Tutoring Schools in Japan: Types, enrollment and cost - Shin Edupower Pvt Ltd